Advertisement
Many people still think of AI as something cooked up in Silicon Valley garages or giant Chinese labs. But India's quietly been building its own stack of language models, too, and it's starting to show. With a mix of academic efforts, government-backed projects, and startups stepping up, the country is finally producing LLMs that understand not just English but Indian languages—something most global models still fumble with.
This list isn’t just about size or hype. It’s about which Indian LLMs are doing something interesting—scale, language coverage, open access, or research value. Here's a detailed look at ten of them.
Built by CoRover.ai, BharatGPT is designed with a strong focus on Indian language support. Unlike most global LLMs, BharatGPT is trained to handle Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, and other regional languages more accurately. It's also aligned with practical use cases—banking, healthcare, and government services. It runs in secure environments and works even without internet access, which makes it attractive for sensitive deployments. While it's not the largest LLM by parameter count, its tight integration with specific Indian use cases sets it apart.
IndicGPT is one of the first LLMs explicitly built to handle multiple Indian languages. Developed under the AI4Bharat initiative at IIT Madras, this model is designed for text generation across languages like Hindi, Telugu, Marathi, Kannada, and more. What’s interesting is that it uses smaller, more efficient models rather than going for sheer size. This makes IndicGPT easier to deploy on local servers without heavy GPU resources. The team behind it is actively improving its language coverage and fluency.

OpenHathi is an open-weight model built by Sarvam AI in collaboration with Microsoft and others. The name is a nod to EleutherAI’s LLaMA series and means “elephant” in Hindi. This model is based on Meta’s LLaMA-2 architecture but trained on Indian data—especially Hindi. It’s one of the few Indian LLMs available in open weights, which is valuable for researchers and smaller startups. OpenHathi is released under a research license, and early benchmarks show strong performance in Hindi reasoning tasks.
Vaani is being developed through a partnership between Sama and the creators of KissanGPT. It is aimed squarely at voice-based AI in Indian languages. This one stands out because it's less about text prediction and more about conversation, especially in agriculture-related fields. It's being trained to understand spoken queries from farmers in rural areas, even with regional accents and background noise. This is less flashy than giant transformer models, but its impact is very real.
Bhashini isn't a single LLM but a national initiative backed by the Ministry of Electronics and IT. It's part of the National Language Translation Mission and builds open models and datasets for Indian languages. The goal is to make all digital content in India accessible in every language. Some of the models under this initiative include translation and transcription engines that feed into digital assistants, government apps, and language learning tools. Think of Bhashini as infrastructure for India's LLM ecosystem.
Kamini is a relatively new LLM being developed at IIIT-Hyderabad. What sets Kamini apart is its training approach: it combines supervised fine-tuning with instruction-following data tuned for Indian contexts. It aims to understand not just Indian languages but cultural nuance. Kamini is being tested on datasets that include legal, medical, and educational content in regional languages. Early versions of Kamini have shown promise in open QA tasks, especially for Hindi and Telugu.
Sanchay is a smaller model built specifically for text classification and tagging in Indian languages. Though not a full-blown generative LLM, it plays an important supporting role. For instance, Sanchay creates clean, labeled corpora that help train larger models. It helps automate dataset creation, which speeds up the training pipeline. It supports over 15 Indian languages and has been integrated into several state-level e-governance apps.

Krutrim is India's first unicorn focused on building full-stack AI products, including its LLM. Developed by Bhavish Aggarwal's AI startup, Krutrim is trained in Indian languages and cultural data. It's meant to be a general-purpose assistant, with APIs planned for businesses, developers, and educational apps. It's still in early release, but early demos show it performing well in Hindi-English code-mixed queries. The startup is planning its hardware integration, which could lead to low-cost AI terminals for India.
Hanooman is a multi-language LLM initiative backed by a healthcare network and three AI startups. At launch, it focuses on 11 Indian languages and promises to expand to 22. The LLM is being developed to make AI accessible to low-income users. It's being built using open-source architectures, focusing on smaller parameter models that can be used on mobile devices. Hanooman’s edge lies in its multilingual training data and a domain focus on public health and education.
Project Varta is a work-in-progress from the Rekhta Foundation, known for preserving Urdu literature. It's building language models focused on Urdu and its intersections with Hindi and Punjabi. While smaller in scope than others on this list, Varta is culturally significant. The model is trained on literary texts, religious discourse, and historical documents. Its aim isn’t just chatbots—it’s digital preservation and interactive search over rare language corpora.
India's LLM efforts focus less on size and more on solving real problems in local languages. These projects are built with India's users in mind, from rural voice assistants to open-weight Hindi models. Whether through government initiatives, academic labs, or startups, the aim is clear: make AI useful across the country's many languages and regions. These models may not grab headlines like GPT-4, but they fill a gap that global models often overlook. That alone makes them worth paying attention to as they keep improving.
Advertisement

XAI’s Grok-3 AI model spotlights key issues of openness and transparency in AI, emphasizing ethical and societal impacts

AI agents aren't just following commands—they're making decisions, learning from outcomes, and changing how work gets done across industries. Here's what that means for the future

How to use os.mkdir() in Python to create folders reliably. Understand its limitations, error handling, and how it differs from other directory creation methods

GenAI is proving valuable across industries, but real-world use cases still expose persistent technical and ethical challenges
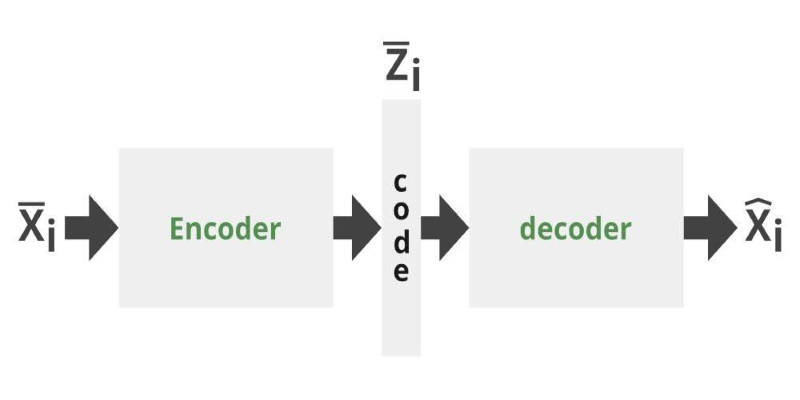
Can you get the best of both GANs and autoencoders? Adversarial Autoencoders combine structure and realism to compress, generate, and learn more effectively
See how Intelligent Process Automation helps businesses automate tasks, reduce errors, and enhance customer service.

The Water Jug Problem is a classic test of logic and planning in AI. Learn how machines solve it, why it matters, and what it teaches about decision-making and search algorithms

How 7 popular apps are integrating GPT-4 to deliver smarter features. Learn how GPT-4 integration works and what it means for the future of app technology

Want to use ChatGPT without a subscription? These eight easy options—like OpenAI’s free tier, Bing Chat, and Poe—let you access powerful AI tools without paying anything

Curious about data science vs software engineer: which is a better career? Explore job roles, skills, salaries, and work culture to help choose the right path in 2025

How mastering SQL with CSVs can improve your data workflow. Use practical queries for cleaning, combining, and exploring CSV files through simple SQL logic

What happens when transformer models run faster right in your browser? Transformers.js v3 now supports WebGPU, vision models, and simpler APIs for real ML use